Vascular Tests
What kinds of vascular tests are most common? What happens when you have one? Will it hurt? Will it mean you need surgery? The following are the most commonly prescribed vascular tests. Be sure to ask your surgeon if you still have questions
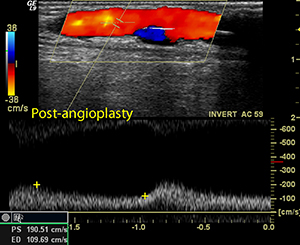
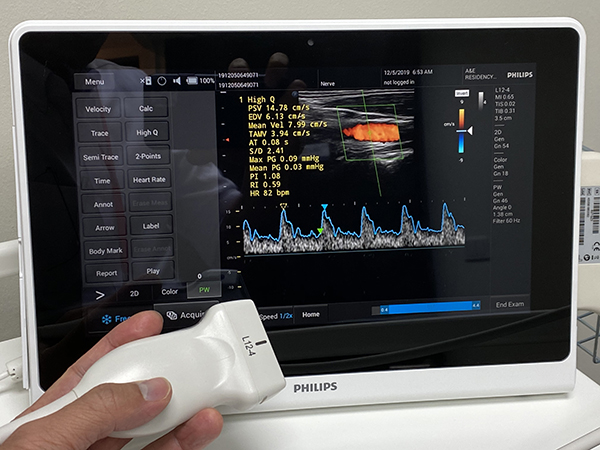
Duplex Ultrasound
Also called: Doppler Test, Vascular Lab Test, Duplex Exam, Duplex Scan, Ultrasound, Ultrasound Exam
Duplex ultrasound is a non-invasive evaluation of blood flow through your arteries and veins. This test provides information to help your vascular surgeon make a sound diagnosis and outline a treatment plan. Accuracy is critical, so ultrasound testing is best performed by a credentialed sonographer in an accredited vascular laboratory.

Carotid Duplex
Also called: carotid Doppler, carotid ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound
This painless, noninvasive test is used to see and measure the rate at which blood flows through your carotid arteries and look for possible blockages. No radiation, dye or needles are used. The test may be performed in a vascular laboratory, a doctor’s office or a radiology department.

Ankle-Brachial Index or ABI Test
Also called: Segmental Pressure Test, Toe Pressure Test, Toe-Brachial Index (TBI)
A non-invasive test that uses inflatable cuffs to gauge circulation (blood flow) and measure blood pressure in the arteries at various locations on the thigh, calf, foot and toes. Done in an outpatient clinic or vascular laboratory. Minimal, brief discomfort, similar to what you feel while having a routine blood pressure test with an inflatable arm cuff.
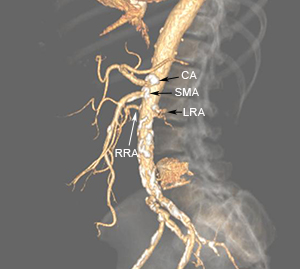
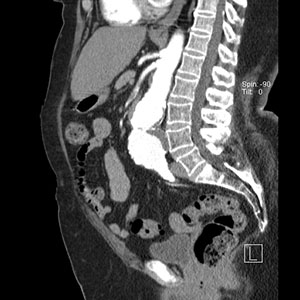
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Tests
Also called: Computed Tomography Angiogram, Computerized Tomography Angiogram, Magnetic Resonance Angiogram
CTA and MRA tests are non-invasive, advanced imaging studies that provide detailed information about the blood vessels within our bodies and their anatomic relationships with other organs. These tests use; modern computerized image processing techniques that let your vascular surgeon view vascular disease 3-dimensionally—an important step in assessing the extent of the disease and how best to treat it.
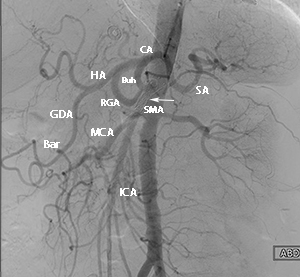
Angiogram
Also called: Angio
An angiogram is an X-ray procedure that can be both diagnostic and therapeutic. It is considered the gold standard for evaluating blockages in the arterial system. An angiogram detects blockages using X-rays taken during the injection of a contrast agent (iodine dye). The procedure provides information that helps your vascular surgeon determine your best treatment options. Angiograms are typically performed while you are sedated. The procedure may last 15-20 minutes or up to several hours, depending on how difficult the test is and how much treatment is needed.
Vascular Tests
What kinds of vascular tests are most common? What happens when you have one? Will it hurt? Will it mean you need surgery? The following are the most commonly prescribed vascular tests. Be sure to ask your surgeon if you still have questions
Duplex Ultrasound
Also called: Doppler Test, Vascular Lab Test, Duplex Exam, Duplex Scan, Ultrasound, Ultrasound Exam
Duplex ultrasound is a non-invasive evaluation of blood flow through your arteries and veins. This test provides information to help your vascular surgeon make a sound diagnosis and outline a treatment plan. Accuracy is critical, so ultrasound testing is best performed by a credentialed sonographer in an accredited vascular laboratory.


Carotid Duplex
Also called: carotid Doppler, carotid ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound
This painless, noninvasive test is used to see and measure the rate at which blood flows through your carotid arteries and look for possible blockages. No radiation, dye or needles are used. The test may be performed in a vascular laboratory, a doctor’s office or a radiology department.

Ankle-Brachial Index or ABI Test
Also called: Segmental Pressure Test, Toe Pressure Test, Toe-Brachial Index (TBI)
A non-invasive test that uses inflatable cuffs to gauge circulation (blood flow) and measure blood pressure in the arteries at various locations on the thigh, calf, foot and toes. Done in an outpatient clinic or vascular laboratory. Minimal, brief discomfort, similar to what you feel while having a routine blood pressure test with an inflatable arm cuff.

Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Tests
Also called: Computed Tomography Angiogram, Computerized Tomography Angiogram, Magnetic Resonance Angiogram
CTA and MRA tests are non-invasive, advanced imaging studies that provide detailed information about the blood vessels within our bodies and their anatomic relationships with other organs. These tests use;modern computerized image processing techniques that let your vascular surgeon view vascular disease 3-dimensionally—an important step in assessing the extent of the disease and how best to treat it.


Angiogram
Also called: Angio
An angiogram is an X-ray procedure that can be both diagnostic and therapeutic. It is considered the gold standard for evaluating blockages in the arterial system. An angiogram detects blockages using X-rays taken during the injection of a contrast agent (iodine dye). The procedure provides information that helps your vascular surgeon determine your best treatment options. Angiograms are typically performed while you are sedated. The procedure may last 15-20 minutes or up to several hours, depending on how difficult the test is and how much treatment is needed.


